What Does a Computer Processor Do? And Other Important Questions
Aug 19, 2019
There are several factors to consider when purchasing a new computer. Some of the primary considerations include storage, memory, and processor speed. You’ll need to find a balance between these three components that will serve your needs and still fall in your budget. You may also be concerned with other features such as graphics capabilities, size, and the type of operating system. When considering performance, consumers tend to focus on just processor speed. However, in this blog we’ll cover how RAM and processors work together to support a computer’s performance.
So What is a Computer Processor?
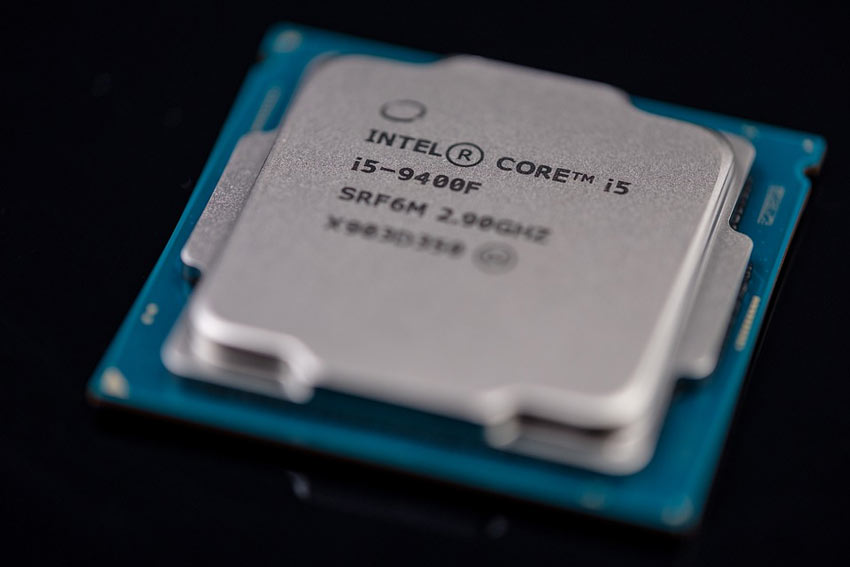

The Central Processing Unit (CPU), or processor for short, is the heart of the computer. It is the computer's main chip and provides instructions for all the other components of the computer. The processor operates like the orchestra leader for the other instruments and is usually a two-inch ceramic square with a silicon chip the size of a thumbnail located inside. The processor lives in the motherboard's CPU socket, which is covered by the heat sink to prevent it from overheating.
A processor's speed is measured in megahertz (MHz), indicating millions of instructions per second, or gigahertz (GHz), indicating billions of instructions per second. However, the computer’s actual speed is not solely a factor of processor speed. Several components influence overall performance but, next to the processor, a computer’s speed is primarily determined by how much Random Access Memory (RAM) is available to perform processes.
What Is RAM?
Random Access Memory (RAM), typically measured in megabytes (MB) or gigabytes (GB), is the computer’s short term memory that stores programs you currently working on. This is in distinct contrast to Read-Only Memory (ROM) that provides permanent storage for your files. Computer hard drives are the most common forms of Read-Only Memory.
Whenever your computer performs calculations, it temporarily holds the data in the RAM until it is needed. Because this memory is short term, you will lose the data if you turn off the computer or close the program without saving it to the hard drive or some other type of ROM. The higher a computer’s RAM capacity, the more processes it can handle simultaneously. As your computer uses more and more RAM, you may notice dips in performance.
Types of Processors
The original CPUs had one core. This meant that the processor chip was made from a single central processing unit. This allowed the computer to carry out one operation at a time. However, modern processors often have several central processing units mounted on a single chip. Computers benefit from multiple processor units by gaining the ability able to run more than one program at the same time. For example, a dual-core processor can run two programs simultaneously, a triple-core processor can run three programs simultaneously, and so on. The more processing units a processor contains, the more programs it can run simultaneously, allowing for faster and more efficient work.
Intel processors contain Hyper-threading Technology, often called Hyperthreading. It is the proprietary Intel technique of splitting single processors into multiple virtual cores to improve its parallel computing capabilities. With hyperthreading, one physical core appears as two processors to the operating system, allowing multiple operations to occur in parallel. This technology allows Intel to provide even more computing power to customers in smaller, more lightweight computers.
Types Of RAM
RAM falls into two categories: Static and Dynamic. Static RAM is a type of semiconductor random-access memory (RAM) that uses a flip-flop memory cell with four or six transistors to store each bit. SRAM cells require more parts than DRAM cells to occupy a lot more real estate on a chip than a DRAM cell.
Dynamic RAM varies from static RAM in that it stores bits in cells consisting of a capacitor and a transistor and must be refreshed periodically. SRAM is faster and more expensive than DRAM. SRAM is typically used for CPU cache while DRAM is usually employed for a computer's main memory.
What To Look For in A Computer
Selecting the right computer for your operational needs requires several considerations. A great processor should be a primary consideration. Modern budget-conscious laptops for personal use usually contain processors with speeds between 1.1 GHz to 2.2 GHz and come with between 4GB and 8GB of RAM. However, laptops designed for gaming or other intensive applications can include processor speeds ranging between 4.5 GHz and 5 GHz with multiple cores and threading, and come equipped with 64 GB of RAM.
Pay attention to how many cores a processor carries as well as whether or not it employs hyperthreading technology. Remember, you could have the fastest processor in the world but insufficient RAM could cripple your productivity. Prices can vary widely between both extremes of the performance spectrum so you will need to carefully consider your operational needs with respect to your budget when making a decision.
EWC Technologies LLC
EWC Technologies offers small form factor computers that feature the best in-class technology. Our NUCs are perfect for both individuals and businesses. To learn more about our company and technology, contact us today.
We take pride in staying abreast of industry news and frequently update our blog with new and relevant content. Ask us about a free demonstration so you can see what makes EWC one of the most trusted providers and integrators of the Intel NUC.


